Overview
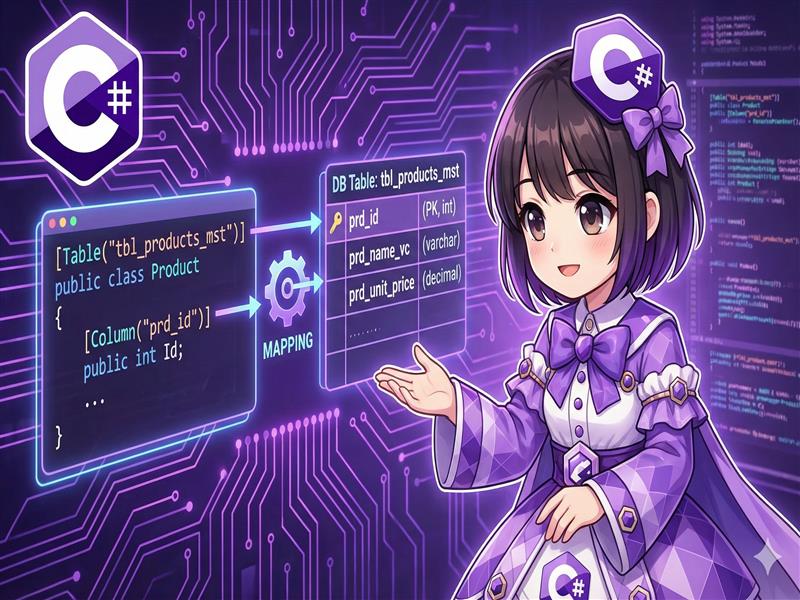
By default, Entity Framework Core (EF Core) treats class names and property names as the names for database tables and columns. However, when working with existing databases or legacy systems, these names often do not match. This guide explains how to use Data Annotations to explicitly map C# class definitions to physical names in the database.
Specifications
- Input: Entity classes and their properties.
- Process: Apply the
[Table]and[Column]attributes to specify mapping targets. - Output: CRUD operations are performed against the specified table and column names.
Basic Usage
Use the System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema namespace to apply the [Table] attribute to a class and the [Column] attribute to properties.
[Table("tbl_employee_master")]
public class Employee
{
[Column("emp_id")]
public int Id { get; set; }
}
Full Code Example
The following code demonstrates a complete console application that maps C# classes (PascalCase) to database naming conventions (such as snake_case) and performs data operations.
Note: Requires the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory package. dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace TableMappingSample
{
// 1. エンティティクラスの定義
// データベース上のテーブル名 "tbl_products_mst" にマッピング
[Table("tbl_products_mst")]
public class Product
{
[Key]
[Column("prd_id")] // 物理カラム名 "prd_id" にマッピング
public int Id { get; set; }
[Column("prd_name_vc")] // 物理カラム名 "prd_name_vc" にマッピング
public string Name { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[Column("prd_unit_price")] // 物理カラム名 "prd_unit_price" にマッピング
public decimal Price { get; set; }
// マッピング指定がない場合はプロパティ名がそのままカラム名になります
public DateTime CreatedAt { get; set; }
}
// 2. DbContextの定義
public class WarehouseContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// 動作確認用にインメモリデータベースを使用
// ※実際のリレーショナルDB接続時にマッピング効果が発揮されます
optionsBuilder.UseInMemoryDatabase("WarehouseDb");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// データの作成と保存
using (var context = new WarehouseContext())
{
var newProduct = new Product
{
Name = "High-Performance Gear",
Price = 2980m,
CreatedAt = DateTime.Now
};
context.Products.Add(newProduct);
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("データを保存しました。");
}
// データの読み込み
using (var context = new WarehouseContext())
{
var product = context.Products.FirstOrDefault();
if (product != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("--- 取得データ ---");
// C#側では自然なプロパティ名でアクセスできます
Console.WriteLine($"ID : {product.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($"Name : {product.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"Price : {product.Price:C}");
}
}
}
}
}
Execution Results Example
データを保存しました。
--- 取得データ ---
ID : 1
Name : High-Performance Gear
Price : $2,980.00
Customization Points
- Specifying Schemas: For databases like SQL Server or Oracle that use schemas, you can specify them using
[Table("TableName", Schema = "dbo")]. - Explicit Data Types: You can also define specific database types using
[Column("price", TypeName = "decimal(18, 2)")].
Important Notes
- Consistency with Existing DB: When using a Code First approach with an existing database, the specified names must match the database exactly. A single character difference will cause a runtime error.
- Case Sensitivity: Depending on the database product (e.g., PostgreSQL), behaviors regarding case sensitivity vary unless names are enclosed in quotes. Remember that the string you specify is reflected directly in the SQL.
- Avoiding Reserved Words: This mapping technique is also useful when you must use SQL reserved words (like
Order,User, orKey) as column names, allowing you to use safe property names in your C# code.
Variations
Using Fluent API
If you want to keep your class definitions clean or use classes from external libraries as entities, you can configure the mapping in the OnModelCreating method of your DbContext.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>()
.ToTable("tbl_products_mst", schema: "dbo");
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>()
.Property(p => p.Id)
.HasColumnName("prd_id");
}
Summary
Use the [Table] and [Column] attributes when class or property names differ from database table or column names. This is an essential technique for converting legacy database naming conventions (like snake_case or abbreviations) into modern C# naming conventions (PascalCase). Since you can also specify data types and schemas, it supports strict database design requirements.