Overview
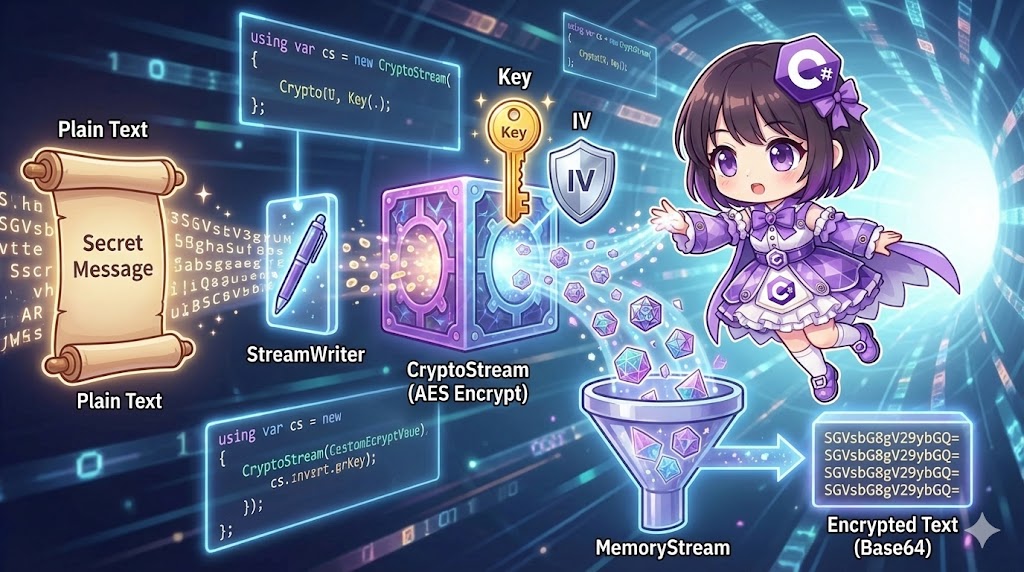
To encrypt strings in .NET, you apply encryption to a data stream using the CryptoStream class. Since strings cannot be encrypted directly, the transformation follows this process: “String → Byte Array → Encryption Stream → Encrypted Byte Array.”
Specifications (Input/Output)
- Input: The plaintext string you want to encrypt.
- Output: The encrypted string in Base64 format.
- Prerequisites: Uses the AES algorithm. The Key and IV can be automatically generated or specified.
Basic Usage
Encryption is performed by layering three types of streams:
- MemoryStream: The base layer that receives the final encrypted data.
- CryptoStream: The filter that encrypts the data as it passes through.
- StreamWriter: The writer that converts the string into the stream.
using var ms = new MemoryStream();
using var cs = new CryptoStream(ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write);
using var sw = new StreamWriter(cs);
// Data flows: sw -> cs (encryption) -> ms (storage)
sw.Write("Secret Message");
Full Code Example
The following class uses the recommended Aes.Create() pattern to handle string encryption.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 1. Instantiate the encrypter (Key and IV are generated automatically)
var encryptor = new StringEncrypter();
string plainText = "This is a secret message for you.";
// 2. Execute encryption
string encryptedText = encryptor.Encrypt(plainText);
// 3. Display results
Console.WriteLine($"Key ({encryptor.Key.Length * 8}bit): {Convert.ToBase64String(encryptor.Key)}");
Console.WriteLine($"IV ({encryptor.IV.Length * 8}bit): {Convert.ToBase64String(encryptor.IV)}");
Console.WriteLine("--- Encrypted Text (Base64) ---");
Console.WriteLine(encryptedText);
}
}
public class StringEncrypter
{
public byte[] Key { get; private set; }
public byte[] IV { get; private set; }
// Constructor: Uses provided Key/IV or generates new ones
public StringEncrypter(byte[] key = null, byte[] iv = null)
{
using var aes = Aes.Create();
Key = key ?? aes.Key;
IV = iv ?? aes.IV;
}
// Method to encrypt a string and return it in Base64
public string Encrypt(string plainText)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(plainText)) return string.Empty;
using var aes = Aes.Create();
aes.Key = Key;
aes.IV = IV;
// Create the encryptor
using var encryptor = aes.CreateEncryptor(aes.Key, aes.IV);
using var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
// The inner using block ensures CryptoStream is disposed of correctly
using (var cryptoStream = new CryptoStream(memoryStream, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
using (var writer = new StreamWriter(cryptoStream))
{
writer.Write(plainText);
}
// At this point, the streams are closed and the final block is written
byte[] encryptedBytes = memoryStream.ToArray();
return Convert.ToBase64String(encryptedBytes);
}
}
}
Customization Points
- Why Base64?: Encrypted data (byte arrays) contains non-printable characters and is not suitable for plain text files or screen displays. Converting to a Base64 string makes it easier to handle.
- Stream Order: The order of
StreamWriter(text) →CryptoStream(encryption) →MemoryStream(storage) is critical. The process will not function if this sequence is altered.
Important Notes
- Closing CryptoStream: You must close or dispose of the
CryptoStreamafter writing all data. This finalizes the encryption process, including “padding” (aligning data to block sizes). Using ausingblock handles this automatically. - Accessing MemoryStream after Disposal: Generally, streams cannot be accessed after being disposed of. However,
MemoryStream.ToArray()is an exception and can retrieve data even after the stream is closed. In the code above, we retrieve the bytes after theWriterandCryptoStreamare finished.
Conclusion
The standard approach for string encryption in C# is to layer multiple streams. By passing the encryption logic from CreateEncryptor into a CryptoStream and writing text into it, encrypted byte data is accumulated in memory. Since the Key and IV are the only way to decrypt this information, they must be stored and shared securely.