-

[Python] Full Control of Mouse Movement and Dragging with PyAutoGUI
Overview This guide explains how to use PyAutoGUI to move the mouse cursor to a specific location or perform drag-and-drop actions. We will cover how to use the duration parameter to make movements look natural and how to choose between ... -

【Python】PyAutoGUIでマウス移動とドラッグ操作を完全制御する
概要 PyAutoGUIを使用して、マウスカーソルを意図した位置へ移動させたり、ドラッグ&ドロップ操作をシミュレーションしたりする方法を解説します。 瞬時に移動させるだけでなく、duration パラメータを使って人間のような滑らかな動きを再現する方法や、... -

[Python] Accurately Get Monitor Resolution and Mouse Coordinates with PyAutoGUI
Overview This is a method to get the current screen size (resolution) and the current mouse cursor coordinates using the GUI automation library "PyAutoGUI." This is a fundamental implementation for identifying click positions and detecti... -

【Python】PyAutoGUIでモニタ解像度とマウス座標を正確に取得する
概要 GUI自動化ライブラリ「PyAutoGUI」を使用して、現在の画面サイズ(解像度)とマウスカーソルの現在地座標を取得する方法です。 自動操作スクリプトを作成する際、クリック位置の特定や、画面端の判定を行うための基礎的な実装となります。 仕様(入出... -

[Python] Basic Recipe for Automating Desktop Operations with PyAutoGUI
Overview This recipe uses the Python library PyAutoGUI to programmatically control desktop operations such as mouse movement, clicking, and keyboard input. This is useful for automating repetitive data entry tasks or GUI testing. We will... -

【Python】PyAutoGUIでデスクトップ操作を自動化する基本レシピ
概要 Pythonライブラリ PyAutoGUI を使用して、マウスの移動、クリック、キーボード入力といったデスクトップ操作をプログラムから自動制御するレシピです。 定型的なデータ入力作業や、GUIテストの自動化などに役立ちます。また、Linux環境(Ubuntu等)で... -

[Python] Creating Histograms and Visualizing Data Distribution with Matplotlib
Overview This recipe uses Matplotlib's hist method to create histograms (frequency distribution plots). We will explain how to draw clear histograms by adjusting parameters like the number of bins, colors, borders, and transparency to un... -

【Python】Matplotlibでヒストグラムを作成しデータの分布を可視化する
概要 Matplotlibの hist メソッドを使用してヒストグラム(度数分布図)を作成するレシピです。 データのばらつきや偏りを把握するために、階級の数(bins)や色、枠線、透明度などを調整して、視認性の高いヒストグラムを描画する方法を解説します。 仕様... -

[Python] Creating Pie Charts in Matplotlib: Adjusting Start Position and Order
Overview This is a recipe for drawing pie charts using Matplotlib. Default pie charts are often difficult to read. This guide explains how to create professional graphs for presentations by setting the data order to clockwise, adjusting ... -

【Python】Matplotlibで円グラフを作成し開始位置や並び順を調整する
概要 Matplotlibを使って円グラフ(パイチャート)を描画するレシピです。 デフォルトの円グラフは見づらいことが多いですが、データの並び順を時計回りにしたり、開始位置を12時の方向に合わせたり、配色を指定したりすることで、プレゼンテーションに適... -

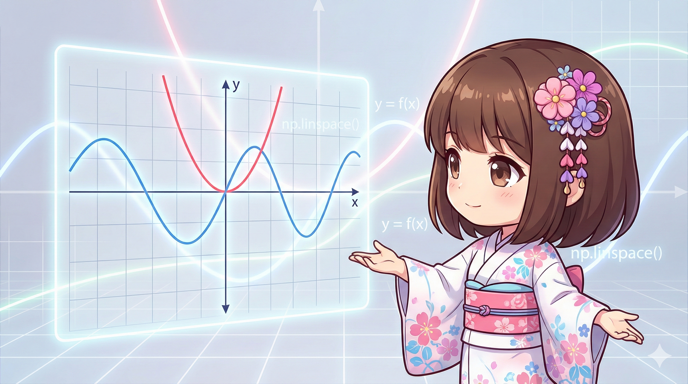
Plotting Function Graphs Based on Formulas with Matplotlib and NumPy
Overview This is a recipe for drawing mathematical function graphs in Python. Instead of entering point data manually, we use NumPy to generate an array for the domain (X-axis). By writing the formula directly into the code, you can effi... -

【Python】MatplotlibとNumPyで数式に基づいた関数のグラフを描画する
概要 Pythonで数学的な関数のグラフを描くためのレシピです。 手動で点データを入力するのではなく、NumPyを用いて定義域(X軸)の配列を生成し、数式をそのままコードに落とし込んで計算させることで、滑らかな曲線を効率的に描画します。 仕様(入出力)... -

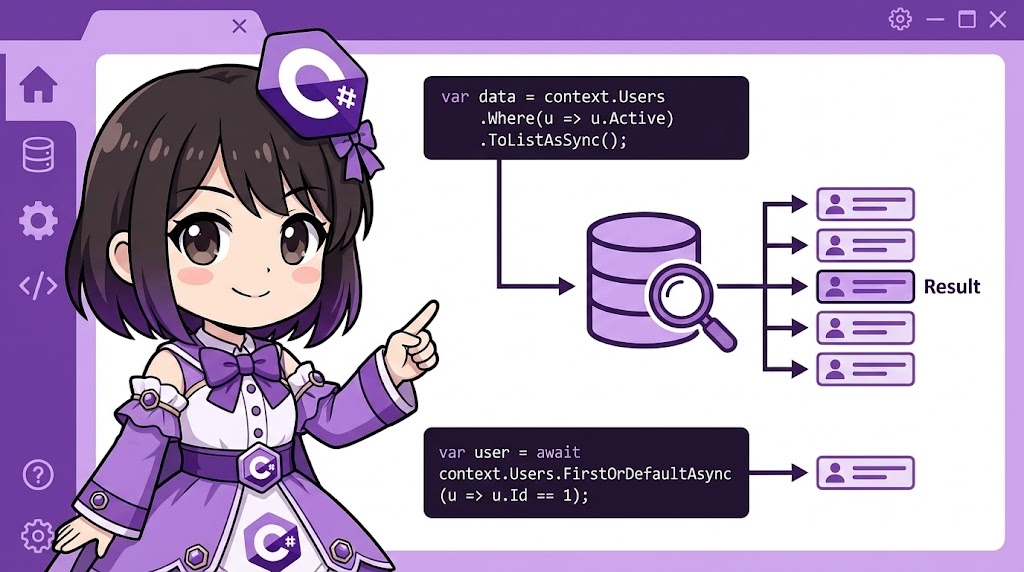
[C#] How to Search and Retrieve Data Matching Specific Conditions in Entity Framework Core
This article explains the basic patterns for retrieving data from a database using Entity Framework Core (EF Core). We will introduce how to implement commonly used queries, such as filtering with the LINQ Where method and searching for ... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreで条件に一致するデータを検索・取得する方法
概要 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) を使用して、データベースからデータを取得する基本的なパターンを解説します。 全件取得だけでなく、LINQの Where メソッドを使った条件による絞り込みや、FirstOrDefaultAsync を使った単一レコードの検索など、実... -

[C#] How to Add Row Data (Records) to a Table with Entity Framework Core
Overview This article explains the basic steps for inserting new rows (records) into a database table using Entity Framework Core (EF Core). In addition to adding a single entity, we will cover how to register data for multiple tables wi... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreでテーブルに行データ(レコード)を追加する方法
概要 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) を使用して、データベースのテーブルに新しい行(レコード)を挿入する基本的な手順を解説します。 単一のエンティティを追加する方法に加え、リレーション(関連)を持つ複数のテーブルに対して、オブジェクト参照... -

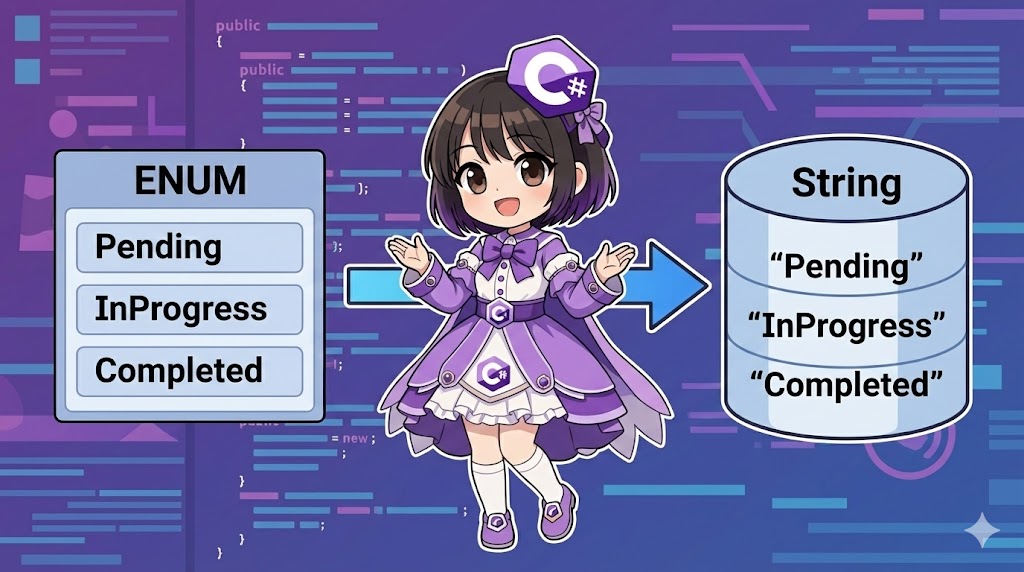
[C#] How to Save Enums as Strings in Entity Framework Core
Overview In Entity Framework Core (EF Core), Enum properties are saved as integers (int) by default. However, you may want to save them as their "name (string)" to improve database readability or to integrate with existing databases that... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreで列挙型(Enum)を文字列としてデータベースに保存する方法
概要 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) では、列挙型(Enum)のプロパティはデフォルトで整数(int)としてデータベースに保存されます。 しかし、データベースを直接参照した際の可読性を高めたり、既存の文字列カラムを持つデータベースと連携したりする... -

[C#] How to Create Column Indexes in Entity Framework Core to Speed Up Searches
Overview Properly creating indexes is essential for database performance tuning. In Entity Framework Core (EF Core), you can use the Fluent API to create indexes on specific columns or apply unique constraints. This article explains how ... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreでカラムにインデックスを作成して検索を高速化する方法
概要 データベースのパフォーマンスチューニングにおいて、適切なインデックスの作成は不可欠です。 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) では、Fluent API を使用することで、特定のカラムに対してインデックスを作成したり、ユニーク制約(重複禁止)を付与... -

[C#] Explicitly Defining Primary Keys and Auto-Increment Behavior in Entity Framework Core
Overview In Entity Framework Core (EF Core), a property named Id is usually treated as the primary key. If the property is a numeric type, the database automatically configures it as an Identity (auto-increment) column. However, there ar... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreで主キーと自動採番の挙動を明示的に定義する
概要 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) では、通常 Id という名前のプロパティが自動的に主キー(Primary Key)として扱われ、数値型であればデータベース側で自動採番(Identity)される設定になります。 しかし、社員コードや商品型番のような「意味を持... -

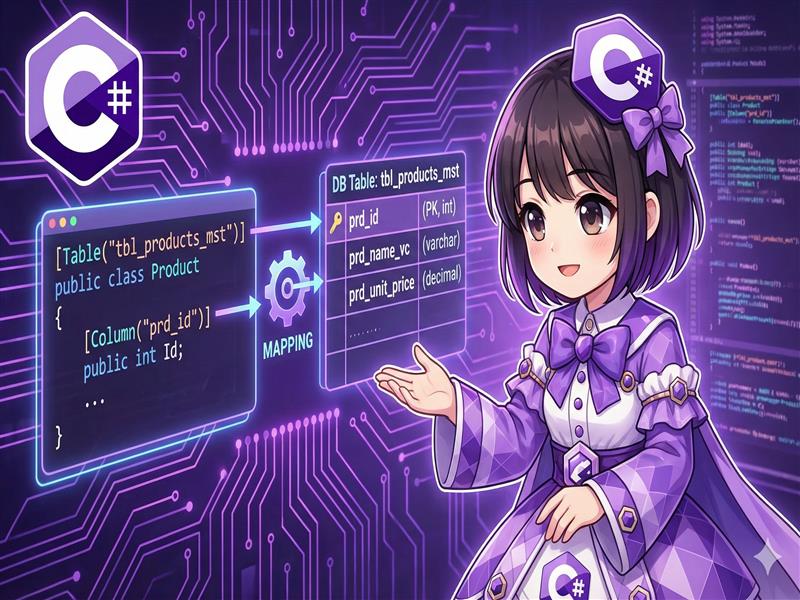
[C#] How to Explicitly Specify Table and Column Names in Entity Framework Core
Overview By default, Entity Framework Core (EF Core) treats class names and property names as the names for database tables and columns. However, when working with existing databases or legacy systems, these names often do not match. Thi... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreでテーブル名とカラム名を明示的に指定する方法
概要 Entity Framework Core (EF Core) はデフォルトでクラス名とプロパティ名をそのままデータベースのテーブル名やカラム名として扱いますが、既存のデータベース(レガシーシステム等)と連携する場合、名前が一致しないことが多々あります。 本レシピ... -

[C#] How to Exclude Specific Properties from the Database in Entity Framework Core
Overview When designing entities with Entity Framework Core (EF Core), you might want to prevent certain properties in a class from being created as columns in a database table. This guide explains how to use the [NotMapped] attribute fr... -

【C#】Entity Framework Coreで特定のプロパティをデータベースから除外する方法
概要 Entity Framework Core(EF Core)を使用してエンティティを設計する際、クラス内の特定のプロパティをデータベースのテーブル列として作成したくない場合があります。 本レシピでは、データ注釈(Data Annotations)の [NotMapped] 属性を使用し、一... -

Plotting Mathematical Functions with Matplotlib and NumPy in Python
Overview This recipe explains how to use the NumPy numerical calculation library to generate smooth sequence data and draw graphs of mathematical functions like quadratic and trigonometric functions using Matplotlib. Instead of creating ... -

【Python】MatplotlibとNumPyで数学関数のグラフを描画する
概要 Pythonの数値計算ライブラリNumPyを使用して滑らかな数列データを生成し、Matplotlibで二次関数や三角関数などのグラフを描画するレシピです。 手動でリストを作成するのではなく、数式に基づいて大量の座標点を自動生成することで、曲線を綺麗に可視... -

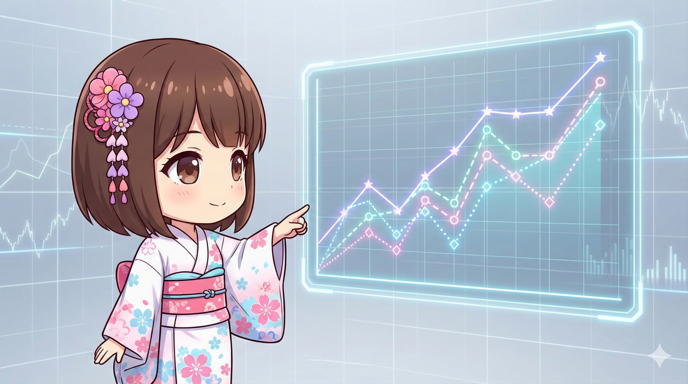
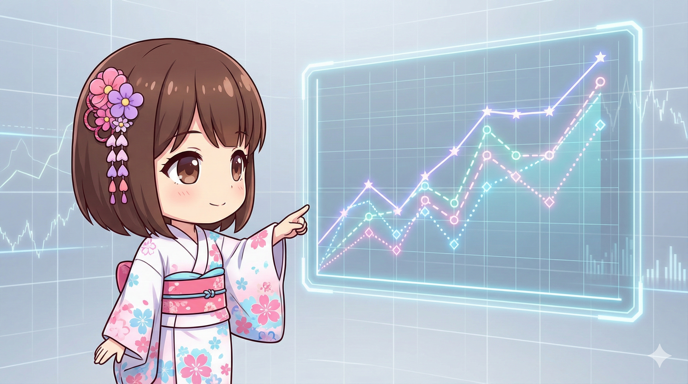
[Python] Customizing Line Plots in Matplotlib: Styles and Markers
Overview This is a guide for creating line plots using the plot method in Matplotlib. Beyond just drawing simple lines, we will explain how to control line styles (solid, dashed), colors, thickness, transparency, and data point markers t... -

【Python】Matplotlibで折れ線グラフを作成し線のスタイルやマーカーを装飾する
概要 Matplotlibの plot メソッドを使用して折れ線グラフを作成するレシピです。 単なる線の描画にとどまらず、線種(実線・点線)、色、太さ、透明度、データポイントのマーカー(記号)を細かく指定し、複数のデータ系列を区別しやすく可視化する方法を...