C++樹林– category –
-

[C++] How to Use std::unique_ptr | Smart Pointers to Automate Memory Management
Introduction When dynamic memory is allocated using new in C++, it must always be manually released using delete. Forgetting to do so causes memory leaks. To solve this problem, C++11 introduced std::unique_ptr, a smart pointer that auto... -

[C++] How to Use std::pair | How to Handle Two Values as a Pair
Introduction When programming in C++, you often encounter data that needs to be treated as a pair, such as "key and value," "first name and last name," or "x-coordinate and y-coordinate." For this purpose, the C++ standard library <ut... -

[C++] What are Static Members? | How to Use Variables and Functions Shared by the Entire Class
Introduction In C++ classes, member variables (data members) usually hold individual values for each object. If you create two objects, car1 and car2, from a Car class, their gas (gasoline level) is managed separately. However, there are... -

[C++] Thorough Explanation of Lambda Expressions | Captures and Generic Lambdas
Introduction When using standard algorithms like std::sort or std::find_if in C++, defining a separate function just to specify a condition can be tedious. Lambda expressions, introduced in C++11, answer the need for "disposable, simple ... -

[C++17] How to Use std::variant | Handling Multiple Types with Type-Safe Unions
Introduction In C++, you may want a variable that can store one of several different types, such as "maybe an int, maybe a string." Conventional unions solve this problem, but they have low type safety because you have to manage which ty... -

[C++] How to Use std::shared_ptr | Smart Pointers for Shared Ownership
Introduction std::unique_ptr in C++ is a smart pointer that guarantees a resource has only one owner. However, there are times when you want to share and use the same object from multiple locations. std::shared_ptr realizes this "shared ... -

[C++] What is a Destructor? | Automatic Cleanup When an Object is Destroyed
Introduction Just as a C++ constructor is an initialization process called automatically the moment an object is "born," a Destructor is a special member function called automatically just before an object "vanishes" from memory to perfo... -

[C++/C] How to Batch Copy (Assign) All Struct Members with =
Introduction In C++ and C structures (struct), there are cases where you want to copy the contents of one variable exactly into another variable. While it is possible to copy members one by one like destination.id = source.id;, this beco... -

[C++] Thorough Explanation of the 4 Types of Casts (static_cast, dynamic_cast, etc.)
Introduction In C++, four different cast operators are provided to perform explicit type conversion (casting), such as converting an int to a double, or a parent class pointer to a child class pointer. These are safer than the old C-styl... -

[C++] What are Inline Functions? | How to Implement Member Functions Inside Class Definitions
Introduction In C++ classes, it is common practice to "declare (prototype)" member functions inside the class definition and "implement (process content)" them outside the class. However, for functions with very short processing, writing... -

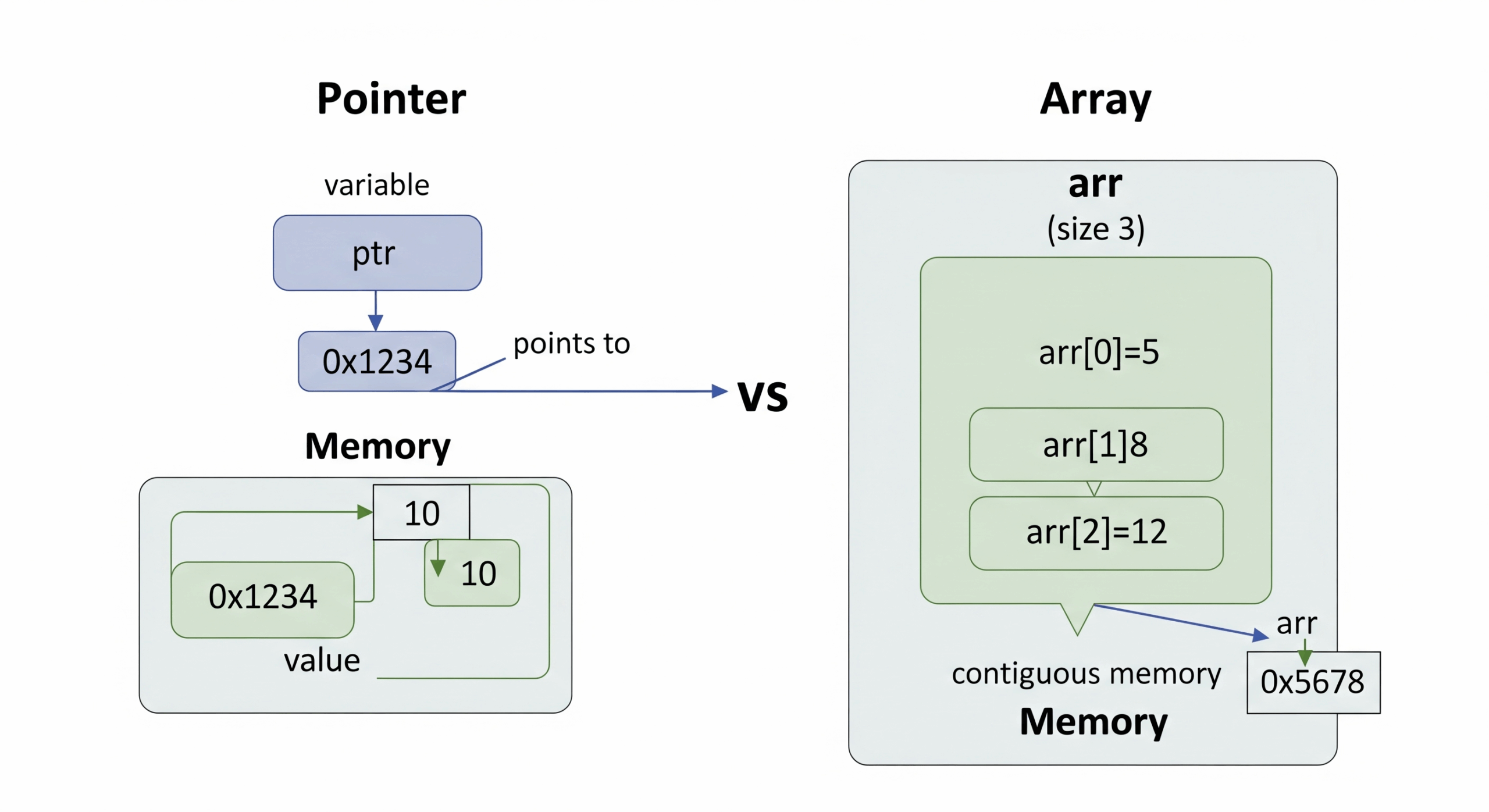
[C++/C] Thorough Explanation of the Difference Between Pointer (const char*) and Array (char[])
Introduction When handling C-style strings in C++ or C, there are two very similar methods: Using a Pointer: const char* ptr = "text"; Using an Array: char arr[100]; These are similar yet distinct, and using them without understanding th... -

[C++] Introduction to Templates | How to Create Generic Functions and Classes
Introduction C++ Templates are a powerful feature that allows you to write generic code by parameterizing types. They not only generalize functions and classes but also dramatically improve the expressiveness of C++, enabling handling of... -

[C++/C] What is typedef? | How to Alias Existing Data Types for Better Readability
Introduction When programming in C++ or C, data type names can sometimes become very long, such as unsigned long long int. Additionally, there are times when you want to distinguish the "meaning" of variables within the program, even if ... -

[C++] How to Use String Streams (stringstream) | Reading and Writing Strings in Memory
Introduction In C++, there are frequent situations where you want to convert numbers to strings, convert strings to numbers, or split a space-separated string into individual words. By using "String Streams" provided by the standard libr... -

[C++/C] Usage of Nested Structures | How to Structure Complex Data
Introduction Structures (struct) in C++ and C are convenient features for grouping related variables into one unit, but their true value is demonstrated when they are nested. You can have a variable of another structure type as a member ... -

[C++] How to Use std::lock_guard and std::unique_lock | Safe Mutex Management
Introduction In multi-threaded programming, if multiple threads access the same data (shared resource) simultaneously, it can lead to data corruption or unexpected race conditions. To prevent this, we use exclusive control (locking) with... -

[[C++/C] How to Use Arrays of Structures | Managing Multiple Records Together]
Introduction C++ and C structures (struct) are useful for grouping related data into one unit, but their true value is unlocked when combined with arrays. By defining an "Employee" structure and then declaring an array of that structure ... -

[C++] How to Use .size() and .length() to Get Character Count of std::string
Introduction When handling std::string in C++, there are frequently situations where you want to retrieve the "length" (i.e., how many characters are contained) of the string. For this purpose, the std::string class provides two member f... -

[C++] How to Use std::thread | How to Create Threads and Execute Functions in Parallel
Introduction Since C++11, the standard library <thread> has supported multi-threaded programming at the language level. This allows you to implement parallel processing, such as performing heavy calculations in the background while... -

[C++] Introduction to Structs | Thorough Explanation from Definition to Initialization and Assignment
Introduction In programming, when you want to manage "Student" information, multiple different pieces of data are related, such as "Student ID (int type)," "Name (string type)," and "Average Score (double type)." Managing these variables... -

Speed Up C++ with Just One Line! Intro to For Loop Parallelization with OpenMP
"Is this heavy loop processing too slow?" In C++ development, the execution speed of computationally intensive for-loops is always a challenge. Modern CPUs usually have multiple cores. It is a waste not to use this power. In this article... -

[C++] How to Use std::tuple | How to Group Multiple Values of Different Types
Introduction In C++, there are cases where you want to return multiple values from a function or temporarily handle data of several different types in a single variable. For this purpose, the std::tuple class was introduced in C++11. std... -

[C++/C] Introduction to Struct Pointers | Getting Addresses (&) and Accessing Members
Introduction One of the powerful features of C++ and C is "pointers." A pointer is a special variable used to hold the memory address where a variable is stored. You can also use this pointer mechanism for structures. By declaring a "poi... -

[Unlocking Performance: Introduction to High-Speed Mutual Exclusion with Atomic]
The most common way to share data safely between threads is locking with Mutex. However, locks can cause thread waiting (blocking) and often become performance bottlenecks. In this article, I will explain atomic operations, a lower-level... -

[C++] Basics of Standard Output with cout | How to Display Text and Numbers on Screen
Introduction In learning C++, displaying results on the console (black screen) to check program behavior and variable contents is the most basic operation. This standard output function is provided by std::cout (short for character outpu... -

[C++20] How to Determine Endianness and Convert Byte Order (std::endian, std::byteswap)
Introduction When exchanging data between different systems, such as in network communication or reading/writing binary files, the difference in Endianness (Byte Order) can be a problem. Endianness refers to the order in which data consi... -

[C++] How to Use noexcept | Explicitly Stating No Exceptions Are Thrown
Introduction In C++, functions potentially throw exceptions. However, there are many functions, such as getter functions or move constructors, that we know "will absolutely not throw an exception." The noexcept specifier, introduced in C... -

[C++17] How to Use std::filesystem::path | Constructing and Concatenating Paths
Introduction The <filesystem> library introduced in C++17 provides the std::filesystem::path class for handling file system paths uniformly. This path object abstracts differences in path separators between operating systems (such ... -

[C++] How to Use std::thread::detach() | Detaching Threads for Background Execution
Introduction In C++, after starting a thread with std::thread, you typically need to wait for it to finish using .join(). However, there are times when you want to "start it and leave it to finish in the background" without the main thre... -

[C++] Introduction to Class Inheritance | How to Create New Classes by Reusing Existing Ones
Introduction "Inheritance" is one of the three pillars of Object-Oriented Programming. It is a powerful mechanism that allows you to define a new class by inheriting the functions (member variables and member functions) of an existing cl...